眼科研究 2000年第4期第18卷 临床研究
作者:马凯 王光璐 张风 孟淑敏 卢宁 马彦
单位:100730北京,首都医科大学附属北京同仁医院眼科
关键词:光学相干断层成像;神经视网膜;黄斑
摘要 目的应用光学相干断层成像(OCT)技术对正常眼黄斑区视网膜神经上皮层厚度进行测定。方法对30只经眼科检查确认的正常眼按同一方法进行黄斑区图像采集,并使用随机软件对其神经上皮层厚度进行测量。将所得数据按距中心点距离和方位进行分类统计计算和检验。结果显著性检验证明测量所得1320个数据具有良好的可信性,且结果与以往类似报道相符。结论OCT能够对视网膜神经上皮层厚度进行精确的量化测定,正常值测定的结果有助于对眼底疾病的理解。
分类号 R774
In vivo measurement of the thickness of neurosensory retina of macula in normal eyes
Ma Kai Wang Guanglu Zhang Feng et al.
(Department of Ophthalmology,Tong Ren Hospital,Capital University of Medicine Science,Beijing 100730)
Abstract ObjectiveTo measure the thickness of the neurosensory retina of macula by optical coherence tomography(OCT)in normal eyes to get criterion for clinical practice.Methods30 normal eyes validated by routine ophthalmic examination were scanned and measured by OCT using the same method.4 scan lines traversing the fovea with the same length and the same angle gap.The thickness of the neurosensory retina on given spots were measured and noted.Results1320 data were collected and grouped according to the distance and directions to the central.Significant test showed that the reproducibility of this process was good.All these results were consonant with the previous reports.ConclusionOCT appears potentially useful for quantitatively characterizing the thickness of the neurosensory retina of macula.The tomographic information provided by OCT eventually may lead to a better understanding of the pathogensis of ocular fudus diseases.
Key words optical coherence tomography neurosensory retina macula
以往有关视网膜厚度的数值多来自于对尸体眼的测量,不但材料有限,且难以避免处理过程中各种因素对正常组织形态的影响。光学相干断层成像(optical coherence tomography,OCT)所具备的高分辨率和无损伤特性使活体状态下视网膜厚度的精确测量成为可能。
1 资料与方法
30只正常眼取自30例因一眼疾患于1998年7~12月间在北京同仁医院眼科就诊、并行OCT检查的患者的健侧眼。其中男15例,女15例,年龄17到53岁,平均39岁,左右眼各15只。患眼疾病包括中心性浆液性脉络膜视网膜病变、Rieger’s病和外伤性黄斑裂孔。
正常眼入选标准:(1)患者无不适主诉;(2)眼科检查(包括裂隙灯显微镜、间接眼底镜、眼底荧光血管造影和眼压)未见异常;(3)裸眼视力大于等于1.0;(4)除外糖尿病、高血压等可能导致眼部改变的慢性全身疾病;(5)患者配合性好,所得OCT图像清晰、可重复性好。
主要设备:ZEISS公司生产的“Optical Coherence Tomography Scanner 2000”系统;国际标准视力表;裂隙灯;间接眼底镜;TRC—50X荧光眼底照相机。
测量和统计方法:通过注视OCT系统设定的内视标,确定被检眼的黄斑中心注视点。选择线性扫描方式,以固定长度4mm的扫描线、以黄斑中心注视点为中心,作间隔45°的线性扫描(图1B),每只眼采集4幅图像。应用随机测量软件对所得图像的视网膜神经上皮层进行测量。数据采集点如下设定:黄斑中心注视点,向两侧距中心距离为50,150,500,1000和1500μm各点(图1A),每只眼41个数据采集点,采集数据44个(中心注视点同一位置重复采集4次)。所有的图像采集和数据的测量均为同一操作者在完全相同的初始条件下以相同的扫描方式获得,原始数据记录只按距中心凹距离标定,排除眼别的干扰,以便在现有条件下尽可能减少系统误差。应用EXCEL软件对正常值范围和可信程度进行估算,并对距中心注视点不同距离和相同距离不同方向的视网膜神经上皮层厚度是否存在显著性差异进行检验。
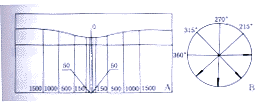
图1A 测量点定位示意图 图1B 扫描方式示意图
Fig.1A Sketch map of measuring spots
Fig.1B Sketch map of scan mode
[1] [2] [3] 下一页 |
